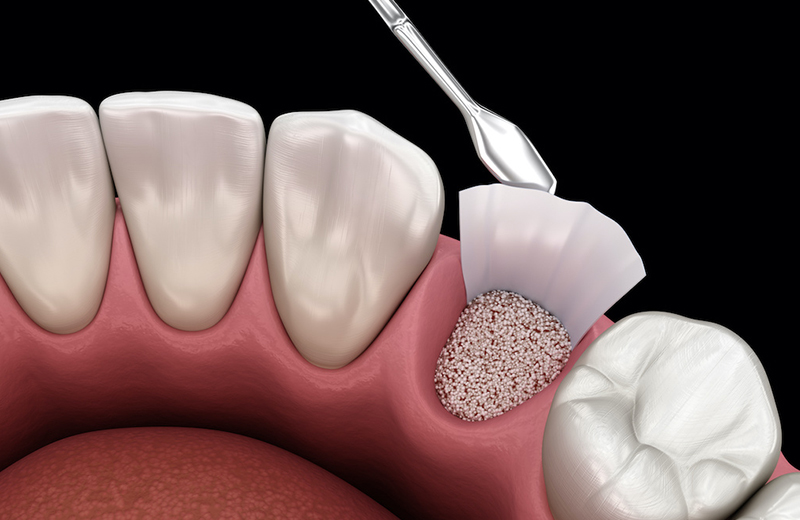
Bone grafting is a procedure used to rebuild areas of the jaw where bone has been lost, specifically to create a stable foundation for dental implants. When a tooth has been missing for some time or was removed without grafting, the jawbone can shrink or become too thin to support an implant.
Types of Bone Grafting We Perform
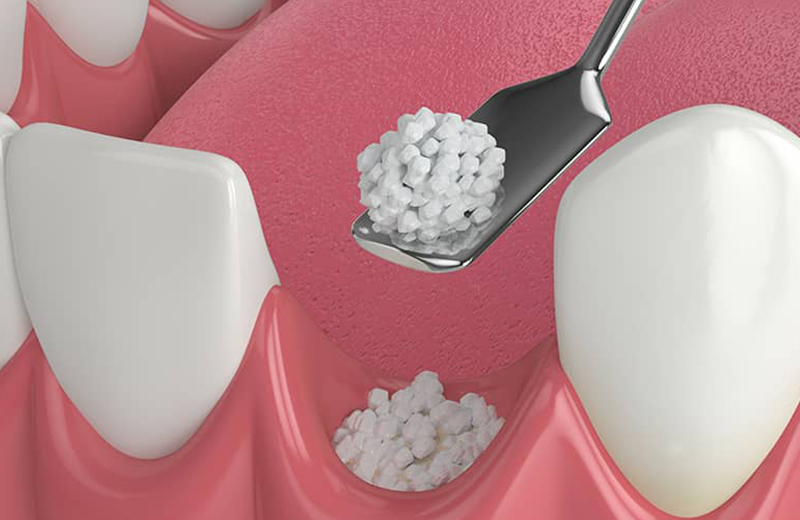
At SFIOS, we specialize in grafting techniques using Allograft (donor) bone, which is safe, biocompatible, and eliminates the need for a second surgical site. Minor Bone Grafting: Small-volume grafts to fill sockets or augment the ridge, often done at the time of extraction or before placing an implant. Major Bone Grafting: Larger-volume grafts to rebuild areas with significant bone loss, typically done as a separate procedure months before implant placement.
Why It Matters
- Dental implants require solid, healthy bone to anchor properly.
- Bone grafting: Restores the bone height and width needed for implants.
- Increases long-term implant stability and success.
- Prevents further jawbone deterioration.
How We Do It
Using 3D imaging, we map out exactly where bone needs to be rebuilt. Grafting is performed under local anesthesia or sedation for comfort. The Allograft bone material is precisely placed, then allowed to heal and integrate with your natural bone.
Recovery and Healing
Minor Grafting:
Recovery is quick, with most patients back to normal in 2–3 days. Healing time before implant placement is typically 3–4 months.
Major Grafting:
Recovery may involve more swelling or discomfort, with 4–6 months of healing before placing implants.
We’ll guide you through every step and monitor your progress closely with follow-up imaging.
